
Survey Methodology Studies Survey Methods
Picking the best survey methodology to conduct your research is essential. The most effective survey research methodology can understand consumer behavior and interpret the world beyond the questions asked. But how do you know what methods are suitable for your project? If you’ve ever asked yourself, what is survey methodology? Keep reading! In this article, we share all the basics you need to know about the methods to write and design great surveys:
What is Survey Methodology?
Survey methodology studies different survey methods to analyze their effectiveness, how to avoid errors, and how to collect the best data. Survey methodology comprehensively covers sampling methods, question types, language and answer options, and set-up strategies like mobile optimization.
Survey Sampling Methods
Survey sampling methods refer to how and where respondents are sourced for survey interviews. There are two main survey sampling methods: probability and non-probability.
Probability Sampling Methods
With probability sampling, each population element has a definite, non-zero probability of being used in the sample. This method guarantees that the sample collected will represent the entire population in that selection. In other words, probability sampling will always involve some kind of randomization. Probability sampling methods include random, systematic, cluster, and multistage sampling.
Non-Probability Sampling Methods
With non-probability sampling techniques, the sample is collected based on specific criteria, so not every member of the population can be selected. Non-probability sampling has no specific probability that any individual will be in the sample set.
These sampling methods are used most often in online surveys. Non-probability sampling methods include quota, convenience, Judgment/purposive, snowball, and voluntary sampling.
Using an online sample marketplace for online survey sampling means researchers can access panelists worldwide via many different supply channels. Our Marketplace Profile page can teach you more about how PureSpectrum sources and categorizes its respondents for any of your non-probability sampling methods.
Survey Question Types and Examples
While many different types of questions can be written for a survey, there are several types we see most often. The nuance in which the question type is presented is a type of survey research methodology. Below are a few common survey question examples:
Closed-Ended Questions
Closed-ended questions pose a question and provide an answer for a participant to choose between. These can be multi-select or single-select. Below is a closed-ended survey question example:
What characteristics are most important when considering [CATEGORY] to purchase? Select all that apply.
[PN: MULTIPLE SELECT, RANDOMIZE]
Price
Value
Brand
Color
Taste
Fit
None of the above [ANCHOR, EXCLUSIVE]
Open-Ended Questions
Open-ended questions ask a question but leave the answer field blank so that a respondent can write whatever they choose as a response. Our Open-Ended Survey Questions article covers open-ended questions examples, tips, and tricks. Below is an open-ended survey question example:
Earlier, you mentioned that you are likely to buy this [CONCEPT]. Why, specifically, are you likely to buy it? Please be specific.
Likert Scale Questions
Likert scale questions are written to scale responses to better understand the degree of likeliness, which helps to better predict respondent actions. They give respondents a range of options, starting at “not at all likely” and scaling up to “extremely likely.” Below is a Likert scale survey question example:
How likely are you to recommend [BRAND] to others?
[PN: SINGLE SELECT, FIXED ORDER]
1 – Not at all likely
2 – Slightly likely
3 – Somewhat likely
4 – Moderately likely
5 – Extremely likely
Slider Questions
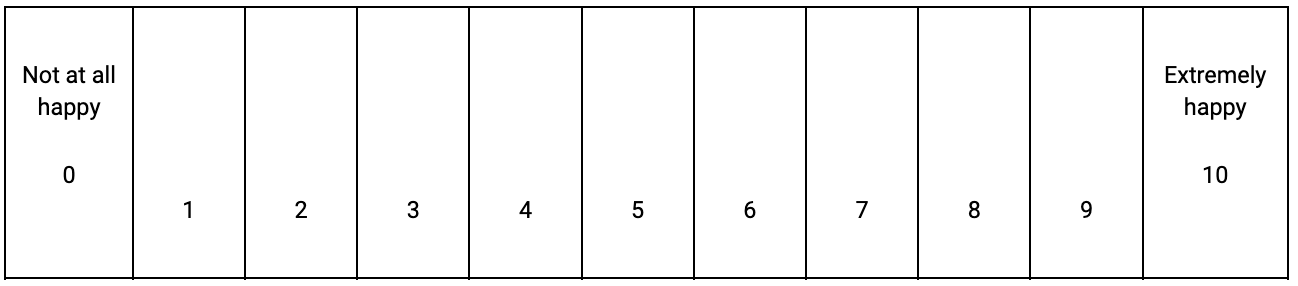
Slider questions use a numerical scale as a way of ranking a respondent’s emotions. This method allows survey participants to move a button along that scale in correlation to how they feel about the idea or concept presented. Below is a slider survey question example:
Thinking about the ad you just viewed, how happy does it make you feel?
[PN: 11-POINT SLIDER SCALE]
Matrix Questions
Matrix questions are a grouping of multiple-choice or single-choice questions displayed in a grid format. The rows present the questions to the respondents, and the columns offer answer choices that apply to each question in the row. These question types can also be used as a way to scale emotions, agreement, or approval of a concept or idea. Below is a matrix survey question example:
When was the last time you viewed any TV shows, movies, or sports via the following devices?
[PN: GRID QUESTION, SINGLE SELECT]
[COLUMNS, FIXED ORDER]
In the last 24 hours
In the past 2 weeks
In the past 30 days
More than 30 days ago
Never
[ROWS, RANDOMIZED]
Television
PC (Laptop or Desktop)
Connected TV (Smart TV, Roku, Apple TV, Chromecast, etc.)
Mobile/Tablet device
Map Style Questions
Heat maps or click maps gauge where on an image or a concept a respondent is most drawn to. Survey participants are asked to select a section of a mapped image in reference to relevance or opinion.
[INSERT MONADIC CONCEPT]
Please click on the part of this concept that is most appealing to you.
[PN: HEAT MAP]
Survey Language Methodology
Survey language methodology studies the way a survey is worded and how it affects the respondent. Gen Pop surveys should use basic wording, be straightforward and stay on one topic. If a survey is stated strangely or contains too many questions, it can cause survey abandonment. Make sure to define complex ideas, acronyms, or industry-specific wording. Keep your survey as short as possible., only asking questions that will be included in the analysis.
Survey language should also be monitored for bias. Many different types of wording biases can occur when crafting a survey. How to Prevent Survey Bias: Causes & Ways to Fix goes more into depth on survey bias.
Survey Set-Up Strategy
How a survey is set up is key to its success. Today most respondents take online surveys on their phones so mobile compatibility must be considered when programming. Mobile optimization can help increase completion rates and your data’s representativeness.
Survey set-up methodology can also advise on how the questions flow into each other and if skip logic needs to be implemented. Skip logic is when a specific response triggers a respondent to not answer another question because they have disqualified themselves from needing to answer it.
What Are the Types of Survey Methods?
Survey research designs are procedures in quantitative research in which researchers field a survey to a sample group to better understand specific demographics, opinions, behaviors, or characteristics of the population.
Online Surveys
Today, most market research is performed via online surveys. With this methodology, questionnaires are dispersed via the internet to a wide range of respondents. Quantitative data is primarily collected.
Telephonic Surveys
With this research methodology, researchers use the telephone for interviewing respondents. Qualitative responses are recorded and logged by the interviewer. Telephonic interviewing is best used when you have very strict respondent requirements and speaking to a person is the best way to evaluate their qualifications.
One-to-One Interviews
This qualitative research method is performed via face-to-face interviews. An interviewer sits with a participant and conversationally asks questions. This type of interviewing is still performed with CEOs, Doctors, and other specialized participants that are hard to find, have time restraints, and would not otherwise be available on online panels. Most of the time these are In-depth interviews (IDIs). These can be done over the phone as well as in person.
Paper Surveys
Before the advent of the internet, many questionnaires were distributed via paper. This type of quantitative survey methodology is less popular today, but still may be useful at conferences, events, or anytime you are looking for immediate and site-specific feedback. However, with the rising popularity of QR codes, surveys can now also be accessed immediately using a cell phone. Paper surveys are also less popular because they require additional costs for data processing and more time to analyze the data.
What Is a Survey Methodologist?
A survey methodologist is an expert in survey design methodology and is brought in to consult on how to optimize a survey experience. They can be consulted for qualitative and quantitative research and should have strong statistical and data analysis skills. A survey methodologist will focus on identifying the population that needs to be sampled for a project and how to reach them best. They can also be responsible for designing questionnaires, and weighing and analyzing the collected data.
Are Surveys a Quantitative Research Method?
A survey can be qualitative, quantitative, or a mix of both methods. When a survey involves a questionnaire with scalable answers, it is a quantitative survey. But if a survey primarily consists of descriptive questions that require in-depth responses, it is qualitative. Surveys that have both types of questions are mixed-method.
Now that you have learned survey sampling methods, question types, and set-up strategies, you are ready to start creating your first survey! The PureSpectrum team is available to assist with your market research at any project stage. We offer Platform Access, Access with Support, and Full-Service solutions.
Let’s get started!
